ECG Reading: Elevate Your Cardiac Care Skills for Heart Health Month

ECG reading is a challenging task for healthcare professionals.
Did you know that 33% of ECG readings are misdiagnosed and could cause life-threatening errors? Learn to save lives this Heart Health Month by mastering ECG interpretation.
As we celebrate Heart Health Month, spotlighting ways to detect and prevent cardiovascular diseases is essential.
The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is one of the most powerful tools. ECG interpretation is a complex but crucial skill for healthcare providers.
Research states that misinterpretations can result in 11% of all patient management errors. But with the proper training and practice, you can gain the knowledge and confidence to avoid this.
This article will cover the basics of ECG interpretation, why it is essential, and how our qualified ECG training can help you provide better cardiac care.
Understanding ECG Reading Basics
An ECG is a graphical display of the heart’s electrical activity.
Consider this like reading a musical score; each wave and rhythm describes the heart’s performance like notes describe how music should sound.
To understand an ECG, let’s break down its key components:
Essential Parts of an ECG Reading
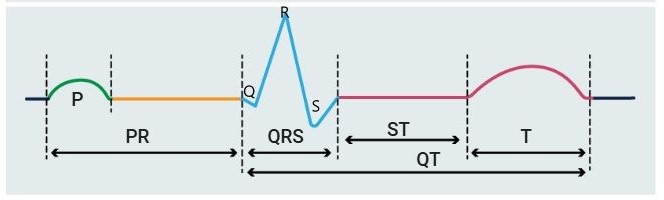
P wave
– This wave represents the atrial depolarization.
– The middle part of this wave represents left and right atrial depolarization.
– The last part of this wave represents left atrial depolarization.
PR wave
– Represents the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization.
– Ranges between 0.12 seconds and 0.20 seconds.
Q wave
– Represents normal ventricular septal depolarization.
– It is considered pathological when it is wide (> 0.04 seconds) and deep (> 2 mm or > 25% of the depth of the R wave).
R wave
– The first positive deflection after a Q or P wave.
– Represents early ventricular repolarization.
RS Complex
– It represents the ventricle’s depolarisation, which is either biphasic or triphasic.
– Ranges from 0.07 to 0.11 seconds.
QT Interval
– The QRS complex starts at the beginning of the QT interval and ends at the end of the T wave.
S wave
– The downward deflection after the R wave
ST Segment
– Represents the end of ventricular depolarisation and the beginning of ventricular repolarization.
T wave
– Signifies ventricular repolarization.
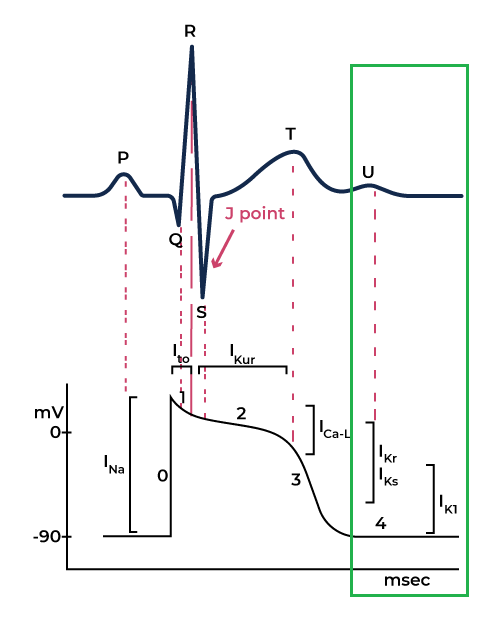
The Cardiac Action Potential: How Electrical Activity Works
The heart’s electrical activity occurs in different phases, which correspond to specific movements of sodium (Na⁺), potassium (K⁺), and calcium (Ca²⁺) ions across heart muscle cells.
Phases of Cardiac Action Potential:
The heart’s electrical activity occurs in different phases, which correspond to specific movements of sodium (Na⁺), potassium (K⁺), and calcium (Ca²⁺) ions across heart muscle cells.
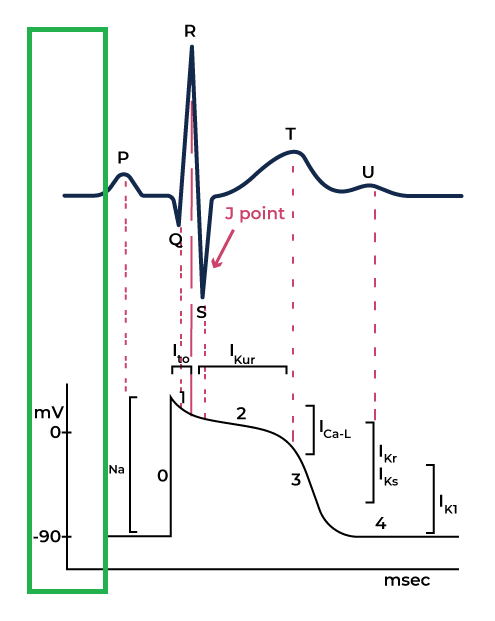
Rest Phase
The cardiac cells are in the rest state and ready to accept an electrical stimulus.
Phase 0 (Upstroke Phase)
Sodium ions enter the intracellular space, leading to brief repolarization. The influx of Sodium ions changes the potential from zero to 30 mV, causing upstroke.
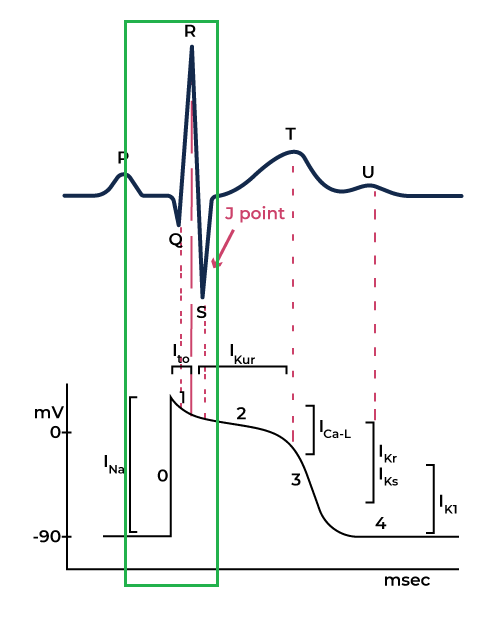
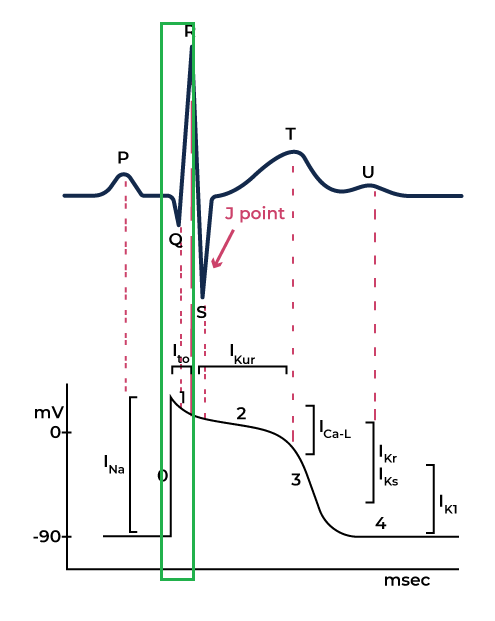
Phase 1
Closure of Sodium channels begins to close while the Potassium channels start to open.
As the potassium ions start to leave the intracellular space, cell voltage across the membrane drops. This corresponds to the J point in the ECG.
Phase 2 (Upstroke Phase)
Voltage across the membrane remains constant. Also, at this stage, the calcium channel opens, causing cardiac muscles to contract This corresponds to the ECG’s ST segment.
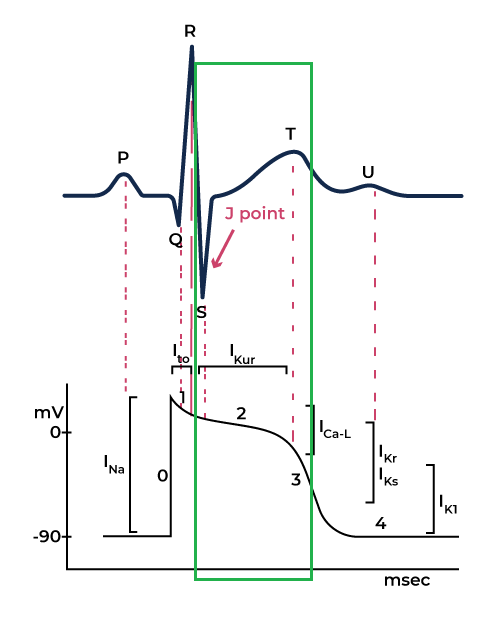
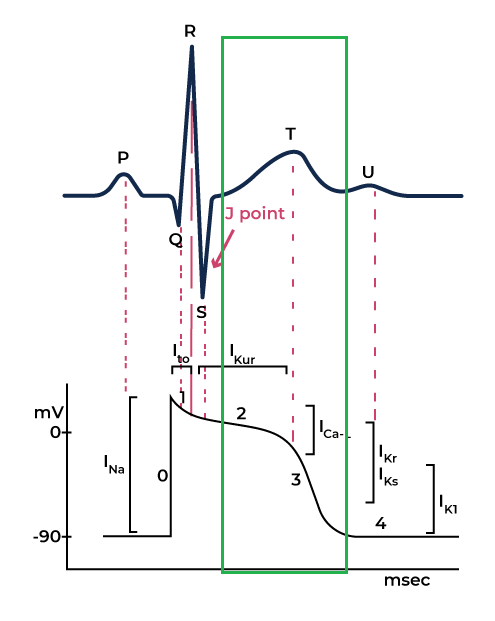
Fase 3 (Repolarisasi Cepat)
Pada fase ini, saluran kalium (K⁺) terbuka sementara saluran kalsium (Ca²⁺) tertutup. Keluarannya ion kalium menyebabkan tegangan menjadi negatif, yang berhubungan dengan gelombang T pada EKG. Sel tetap dalam keadaan istirahat kecuali ada stimulus yang terjadi.
Phase 4
The cell repolarized in phase 3 and is now in the resting stage. The potassium and sodium ions are back to their respective spaces, which is considered as zero membrane potential.
The Importance of Accurate ECG Reading
Imagine you are an ER nurse caring for Mr. Thompson, a 65-year-old patient recovering from colon surgery. Looking at the ECG monitor, you observed unusual readings: tachycardia, flattened T waves (hinting at hypovolemia), and ST segment depression (a sign of reduced oxygen delivery to the heart).
These changes are concerning. You connect the dots, and find that his symptoms and ECG findings point to potential acute bleeding, a critical complication in the postoperative phase.
You initiate fluid resuscitation per your hospital’s protocol while alerting the surgical and anesthesiology teams.
Beyond emergencies, ECG skills are invaluable for monitoring at-risk patients and ensuring early intervention for potential issues. Misinterpretations can lead to delayed diagnoses, incorrect treatments, and even fatal outcomes. That’s why mastering ECG reading is not just a skill, it’s a responsibility.
Benefits of an ECG Training
Our ECG training course is designed to help healthcare professionals like you improve your ECG interpretation skills. Here’s how it can benefit you:
✅ Improved Diagnosis:
With the availability of online ECG training courses, emergency medical personnel are becoming more skilled at accurately reading ECG recordings.(Huitema et al., 2019)
✅ Increased Confidence:
Through proper ECG training, healthcare providers can enhance their abilities and knowledge, giving them the confidence to interpret heart rhythms effectively.
✅ Better Care Outcomes:
EGC Courses provide healthcare workers with a systematic approach to reviewing ECGs, which aids in making informed management decisions for their patients.
✅ Real-Life Application:
Imagine you’re a nurse in the ER, and a patient arrives complaining of chest pain. The ECG shows an ST elevation, which could mean a heart attack. Your ability to interpret the ECG quickly and accurately could save their life!
What You’ll Learn in Our ECG Training
📌 Mastering ECG Basics:
- – Learn to identify key parts like P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves.
- 📌Applying ECG in Real-life Scenarios:
- – Practice with interactive case studies and real-world examples.
- – Develop the confidence to act quickly and accurately in emergencies.
- 📌Flexible and Practical Learning:
- – Access online courses designed to fit your busy schedule.
- – Earn Kemenkes certification and SKP credits to advance your career.
Why Choose Our ECG Training?
- Affordable and Certified: Our course is Kemenkes-certified, ensuring high-quality training.
- Career Advancement: Earn SKP credits and add value to your expertise.
- Designed for Healthcare Professionals: Whether you’re a nurse, midwife, or doctor, this course is tailored to your needs.
Celebrate Heart Health Month with Skill Enhancement
Heart Health Month is the best time to invest in yourself and your patients. Join our certified ECG training, and you will gain the confidence to make life-saving life decisions.
Don’t miss this opportunity to level up your cardiac care abilities!
Together, we can improve patient outcomes and celebrate Heart Health Month with meaningful action.
📌 Enroll today and take the first step toward mastering ECG interpretation.
References
- Abdullah, L. A., & Al-Ani, M. S. (2020). CNN-LSTM Based Model for ECG Arrhythmias and Myocardial Infarction Classification. In Advances in Science Technology and Engineering Systems Journal (Vol. 5, Issue 5, p. 601). Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal (ASTESJ). https://doi.org/10.25046/aj050573
- Breen, C. J., Kelly, G. P., & Kernohan, W. G. (2022). ECG interpretation skill acquisition: A review of learning, teaching and assessment. Journal of electrocardiology, 73, 125–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelectrocard.2019.03.010
- Islam, T., Kundu, A., Ahmed, T., & Khan, N. I. (2022). Analysis of Arrhythmia Classification on ECG Dataset. In 2022 IEEE 7th International conference for Convergence in Technology (I2CT) (p. 1). https://doi.org/10.1109/i2ct54291.2022.9825052
- McGrath, Anthony, and Michael Sampson. “Electrocardiograms: A Guide to Rhythm Recognition for Emergency Nurses.” Emergency Nurse, vol. 26, no. 1, 10 May 2018, pp. 21–29, https://doi.org/10.7748/en.2018.e1767.
- Wei, Xingyu, et al. “Physiology, Cardiac Repolarization Dispersion and Reserve.” PubMed, StatPearls Publishing, 2023, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537194/





